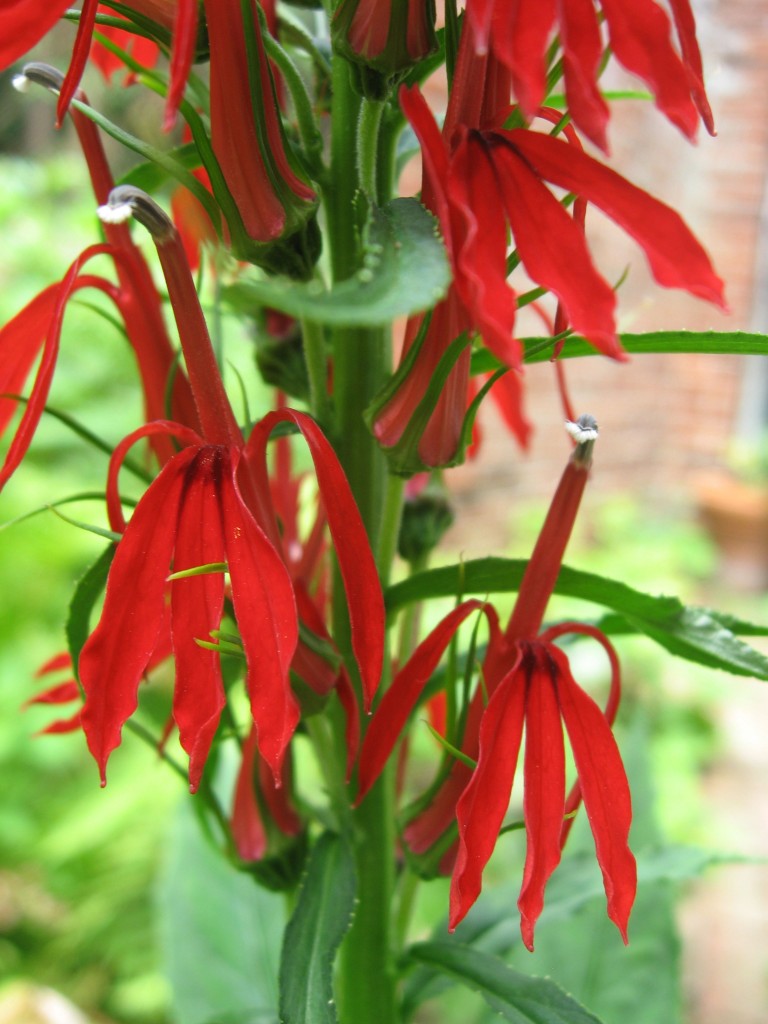
This Lobelia cardinalis was a pleasant surprise. Â We had planted it in various places in the yard where it would last a year or two, producing seed and great flowers only to disappear. Now it’s reappearing in a place we did not expect. Â Now we have to walk over it as it is growing so close to the brick walkway it is covering it.
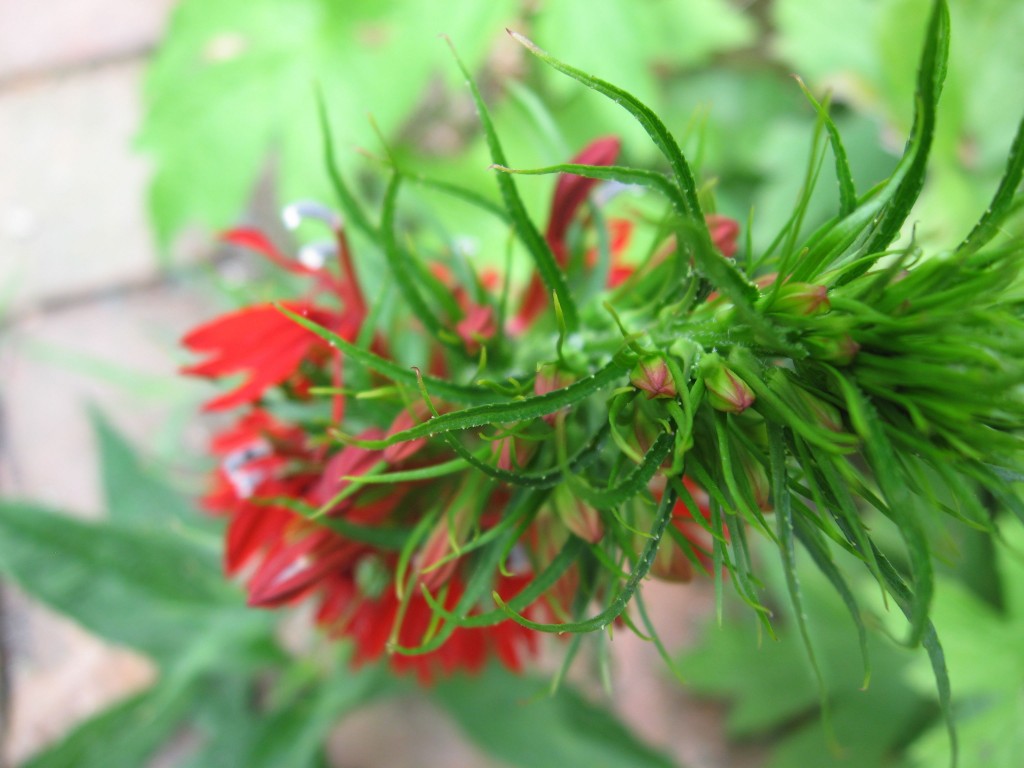

This flower is so red it cannot be matched and a picture does not fully show off the deep red color. Â In the shade, this flower glows and the red color is magnificent.
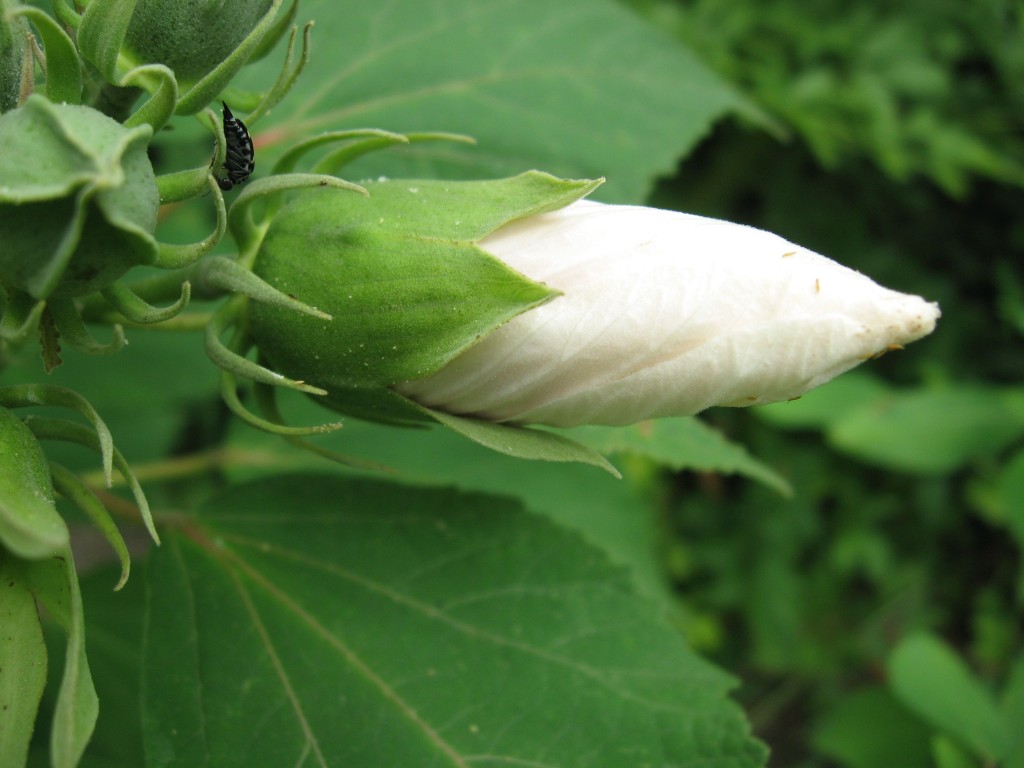

This is the Hibiscus mosheutos, ready to open. The flower is six inches in diameter. Â This one likes its feet wet as well as a sunny location. After a flowerless season in the shady front yard, Isabelle had the idea to place it in the sunny backyard next to the drainpipe. Â Now it is flowering.
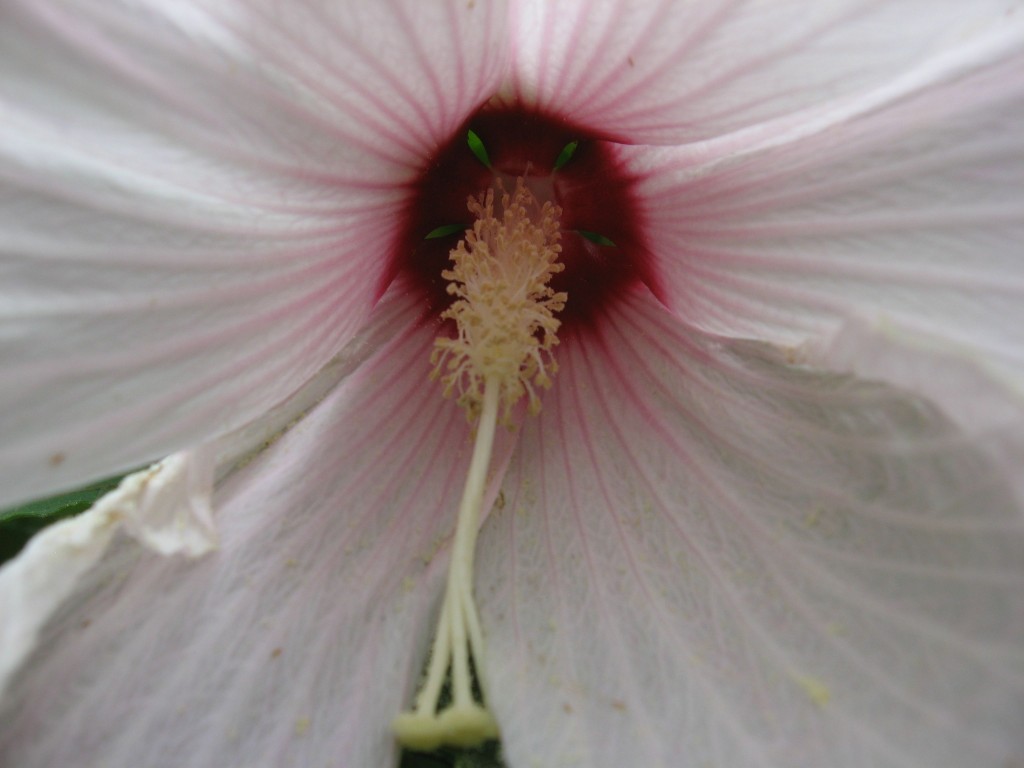

Each flower lasts only two days, but the plant produces so many flowers that there are plenty to appreciate on any given day.
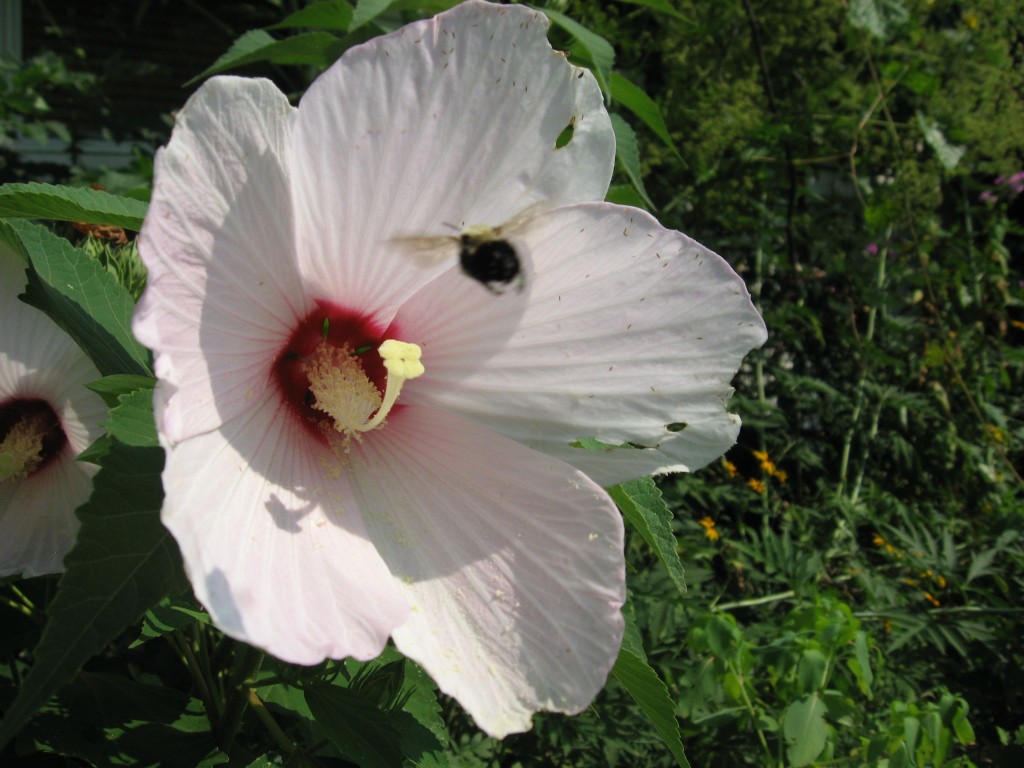

The bees love this flower and were cycling around it every few seconds making a photograph possible.
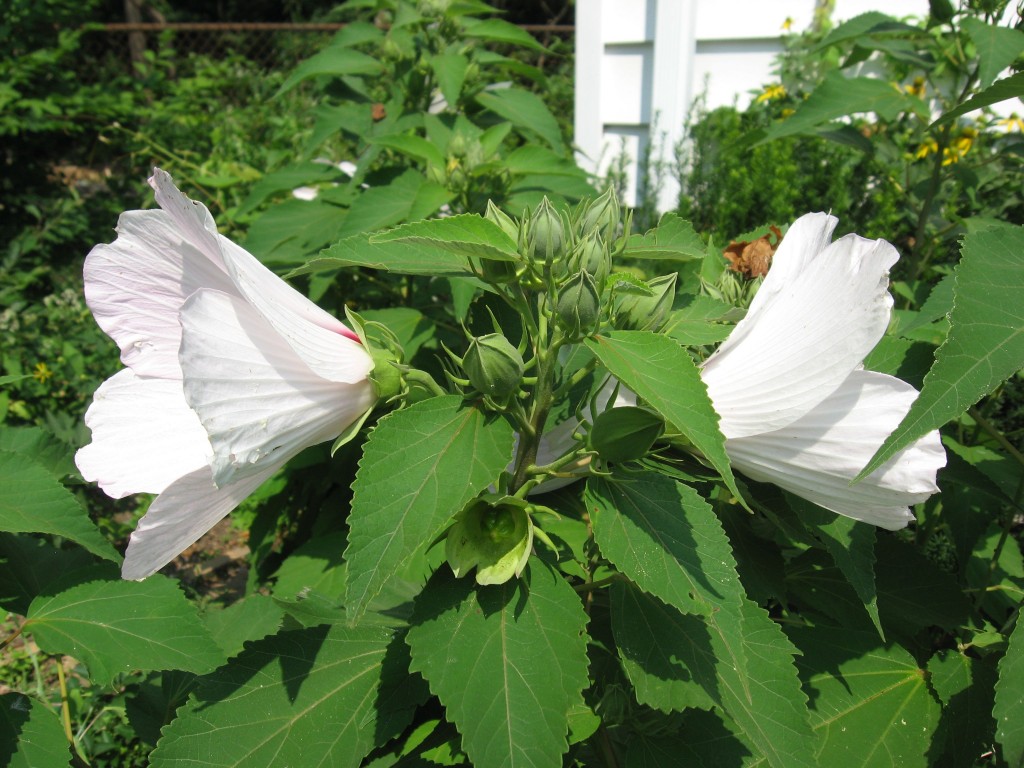

Here are two blooming Hibiscus moscheutos flowers with ones on the way in the middle. The lower one has already bloomed and is on its way to producing seed, the flower having fallen off.
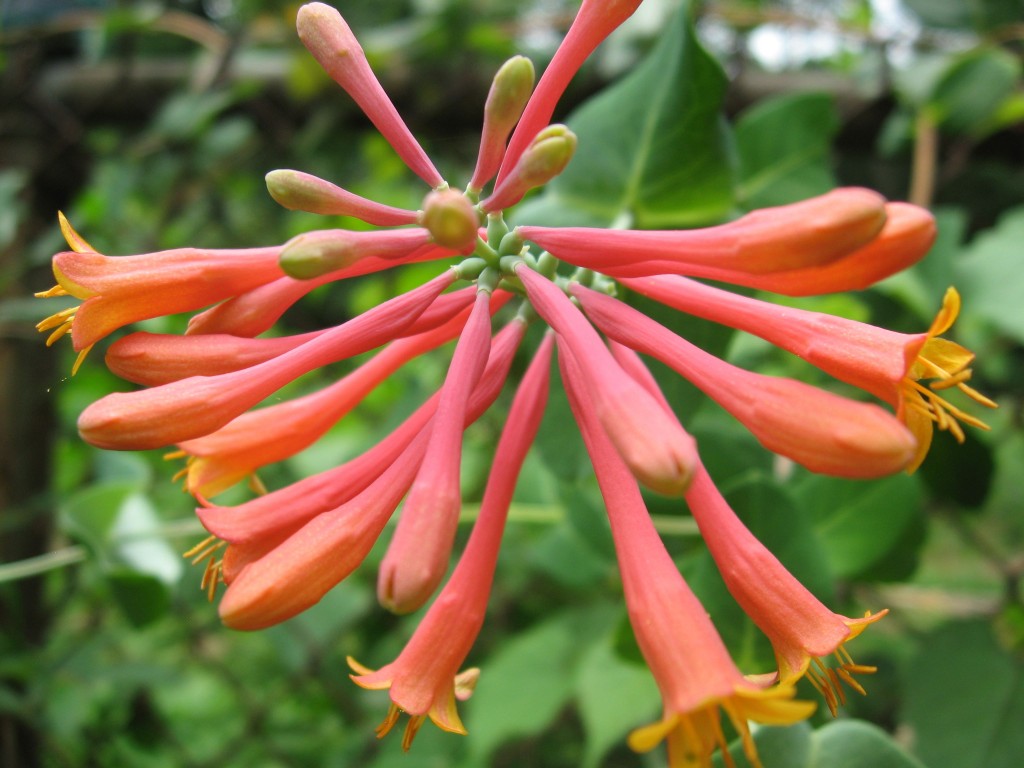

This native honeysuckle is a flower factory.  It has been cranking out flowers all summer.  The Hummingbirds have been visiting this flower all day every day.  Strategically planted right outside the window, we can watch the hummingbirds from the comfort of the couch.  The Hummingbirds rough up the flowers which fall off often. Our summer mornings are not complete without coffee, Lonicera sempervirens and Hummingbirds.  The  red Lobelia is also attracting the hummingbirds, which is growing at the foot of the honeysuckle vine.
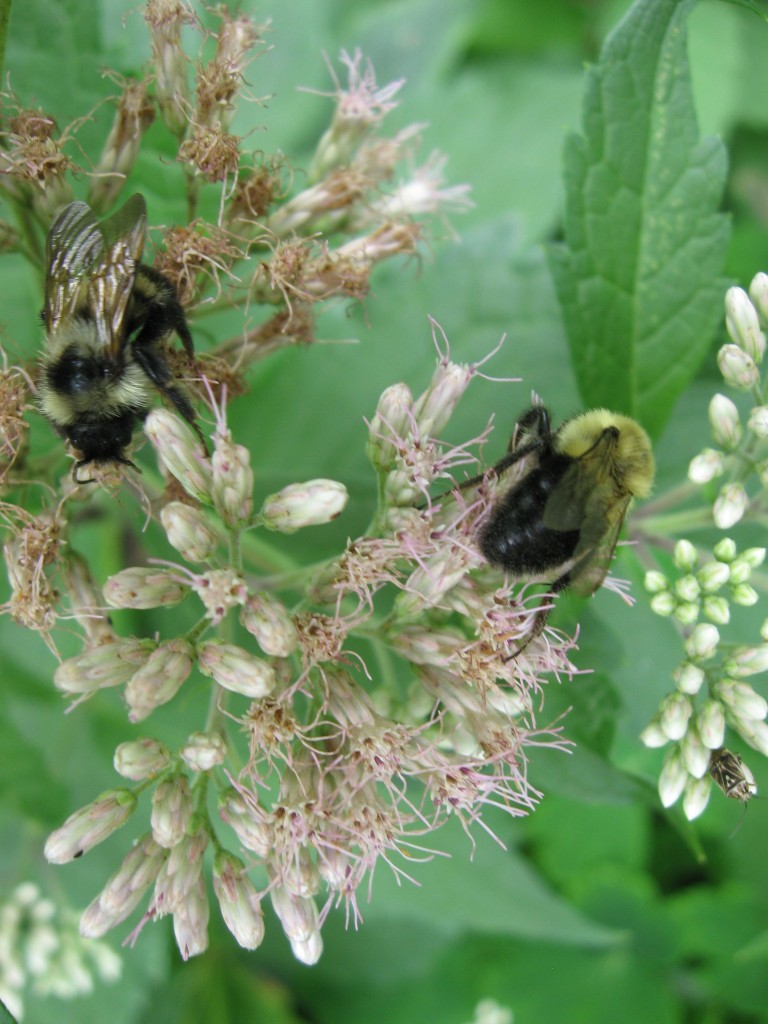

If the word weed in the common name Joe-pye-weed is discouraging to you in your plant selection process and this great flower is passed by, you are missing out. We have two Joe-pye weeds, Eupatorium purporeum and Eupatorium fistulosum for starters. Â This is a stately and entertaining plant and does not behave like a weed at all. Â Bees love it, as the above picture shows, and it has an ornamental value. Â It is versatile and drought tolerant. Â The leaves have a soft inviting texture and the flowers have subtle tones of pink that look great against the backdrop of summer green.